Welcome to the most in depth 3D printer filament buyer’s guide on the internet. This guide covers everything you need to know about 3D printer filament.
There are 11 sections in this guide, and each section gives an overview of the topic. But every section of this guide will lead you to an article with more in depth infromation so you can learn more if you want to.
Also, check out our huge list of dozens of filament brands with reviews and information to help you make an informed purchase. Combined with this guide, you will have all of the information you need to buy 3D printer filament.
Here are the best filaments on the market right now:





PART 1: Introduction To 3D Printer Filaments

What is 3D Printer Filament?
3D printer filament is the strands of plastic wire that go into a printer’s extruder. The extruder melts and extrudes the filament onto the print bed to form objects.
In comparison to 2D printers, filament basically acts as the ink of your 3D printer, except in three dimensions.
3D Printer Filament Uses
3D printer filaments can now be used to make everything from medical devices and electronics to functional parts for commercial mechanical applications.
In fact, 3D printing is so much more efficient for prototyping and custom part production that it has virtually taken over the commercial prototyping industry.
It makes sense: 3D printing offers much more effecient ways of constructing many complex shapes and machines than traditional manufacturing processes.
Innovative 3D Printer Filaments Brands
Thankfully, because the filament industry has boomed over the last decade along with rise of 3D printers, lots of exciting things are happening in the filament industry.
As a result of years of research by engineers around the world, there are now dozens of innovative filaments for almost any application.
Pellets, Powers, and Resins
There are many different types of 3D filament plastic available at the moment, and new types of filament are created practically every month.
For information about filament and other forms of plastic used in the 3D printing, such as pellets and resins, check out ‘Pellets, Powders, And Other Forms Of Plastic Used In 3D Printing‘ where we go over the other common forms of 3D printing plastic materials.
PART 2: Buying 3D Printer Filament

Buying filament is usually a pretty simple process. But figuring out which brand to buy from is trickier since not all of them are high quality.
Check out our gigantic list of dozens of filament brands for reviews and information about each brand before buy.
What should you look for in a brand?
The main thing a 3D Printer Filament Buyer’s Guide should tell you is how to find good quality filament.
There are three things you should look for in a filament brand:
- Filament quality
- Consistency of the tolerance
- Price
These are the three main factors that usually determine whether or not you will have a good experience with a brand’s products.
There are several other aspest to consider about a brand as well, though, such as packaging and customer service, but those are usually less important.




Obviously you want to buy the highest quality filament you can. The quality of filament directly affects the quality of your print. There are tons of cheap Chinese filaments that are very poor quality.
We suggest avoiding them. Otherwise you are bound to spend your time unclogging your extruder and dealing with poor quality prints.
Cheapest 3D Printer Filament
 The price of filament depends loosely on many factors including the quality and source. The reason we say ‘loosely’ is that, at the end of the day, the price is determined mostly by manufacturers and suppliers based on what they think people will buy.
The price of filament depends loosely on many factors including the quality and source. The reason we say ‘loosely’ is that, at the end of the day, the price is determined mostly by manufacturers and suppliers based on what they think people will buy.
That means you can often find poor quality filament for high prices (like cd-writer.com or Cool Components ), and high quality filament for low prices like (Amphilogic and FormFutura). Check out our list of the cheapest filaments here.




Tolerance
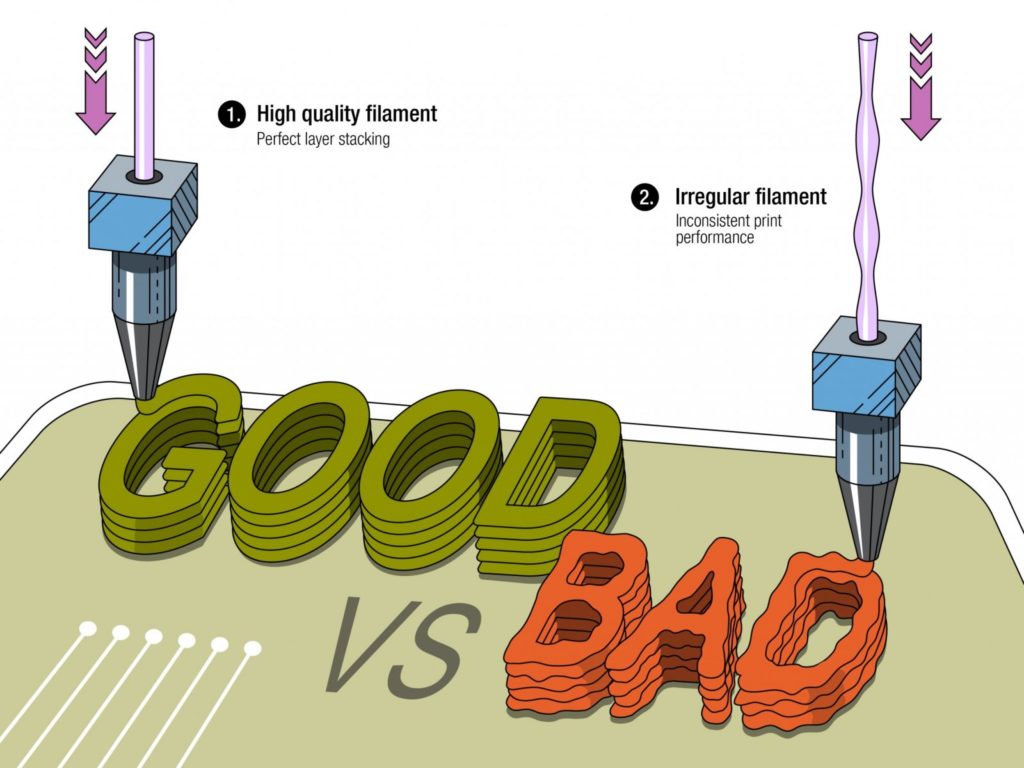
Tolerance is probably the single most important factor to look at when evaluating a brand. If a filament has bad tolerances, then it basically unusable.
Watch out for cheap chinese filaments that often have terrible tolerances. These brands are everywhere and many beginners fall for them.
Instead, stick with brands that have incredible tolerances. For instance, Hatchbox offers tolerances as low as +/- 0.01 mm, which means that their tolerances are basically perfect.




PART 3: Types of 3D filament

As the world of 3D printing grows, more types of filament are coming to market every year. In fact, there are now dozens of types of filament available today.
The selection will only increase as 3D printing finds new applications. There are some very interesting filaments out there, including algae filament by Algix and flexible wood filaments by Lay Filaments.
Check out a full list of types of filament in the ‘2019 3D Printer Filament Materials Guide‘ for more information.
What are the most popular types of filament?
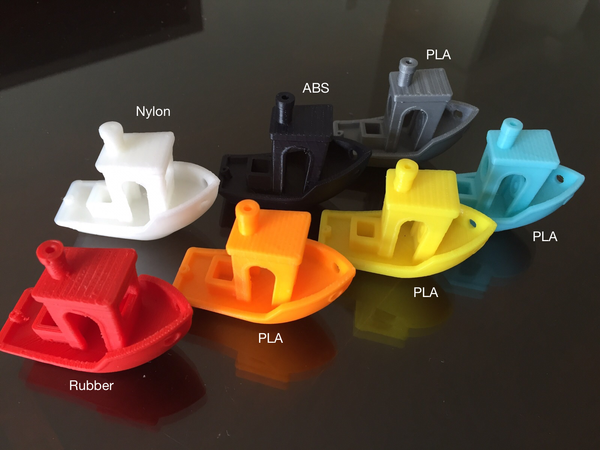

Currently, the most popular types of plastic filaments are PLA, ABS, PET, TPU, Nylon, Glow in the Dark, Metal, and Wood.
They each have different properties and have different applications.
PLA Filament
- PLA is the most popular plastic used in 3D printing and is easy to work with.
- It is a hard plastic that can be used to print most non-functional plastic objects, such as figurines, jewelry and pencil holders.




ABS Filament
- ABS can be used to create parts for machines, toys for kids, and even medical devices.
- The only major downside to ABS is that it is a bit harder to work with than PLA.



PETG Filament
- PETG is also growing in popularity.
- It is very strong and as easy to print with as PLA.





Here’s a prediction: due to the fact that PETG has the strength of ABS and ease of PLA, there is a good chance that it will take over as the most popular filament material in the future.
Check out a full list of types of filament in the ‘2019 3D Printer Filament Materials Guide‘.
PART 4: 3D Printer Filament Glossary of Terms

3D printers are technical machines and they require good quality filaments to produce good quality prints. But how do you evaluate filaments and decide what to buy?
There are certain things to look for when choosing a filament, and 3D printer enthusiasts use a bit of jargon to describe them. It will be important to understand a few basic terms before moving on to the rest of the article.
You can find a complete list of 3D printer terms in our glossary.
You can also check out the Glossary of Terms for a complete list of 3D printing terminology.
PART 5: Homemade filament

The irony of buying filament is that plastic waste is everywhere around us these days. Wouldn’t it be great if we could recycle that waste plastic into filament?
With home filament extruders, you can do just that. It takes a little bit of work to learn how to produce usable filament with these machines.
But once you do, you can start recycling plastic bottles, milk jugs, and other commonly available plastic items into filament for your 3d printer. You can also purchase plastic pellets for fraction of the price of filament and extrude them into filament yourself.
Table could not be displayed.Of course, these machines aren’t cheap. A typical filament extruder will cost you anywhere from $500 to $2000.
But if you plan on doing a lot of printing, then you might want to seriously consider getting one. After all, you would only have to extrude about 50 rolls of filament to recoup the value of investing in $1000 extruder.
Filament extruders

There several great filament extruders you can buy for your workspace. They each have pros and cons.
The best option currently is probably the filabot extruder simply due to ease of use. But here is a list of other filament extruders worth considering:
Filament winders

Another machine that dovetails nicely with filament extruders is filament winders. These machines wind the filament onto a spool at a constant speed as it comes out of the extruder.
One of the hardest parts of extruding your own filament is making sure that you don’t pull too hard on the filament during winding as it comes out of the extruder. Otherwise, your filament will have uneven diameters.
Filament winders make it much easier to exert a constant low level force on warm filament without messing up the tolerance.
How to make 3d printer filament yourself
Once you have all the components, it’s relatively straightforward to make filament yourself.
Check out our guide to making 3D printer filament at home.
PART 6: How to store filament
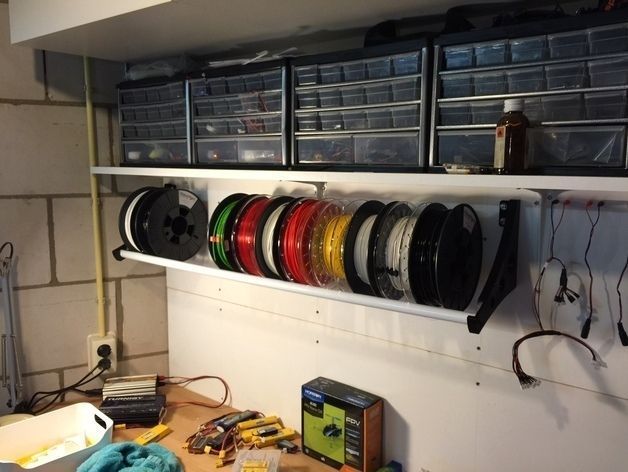

The best way to store filament is is in a storage bin. You can by these plastic storage containers at office supply stores, large department stores like Target and Walmart, as well as some Hardware stores.
Make sure you get storage containers that have air-tight lids to prevent humidity from getting inside.
Also, try to get clear bins if you can so that you can see what filaments are inside without opening it up. It’s not necessary but it makes life a bit easier.
 Next put a desiccant of some kind in the bin. A popular desiccant is a porous bag of rice.
Next put a desiccant of some kind in the bin. A popular desiccant is a porous bag of rice.
Rice naturally absorbs moisture from its environment. So if you put a few cups of rice in a sock or shoe box and place it in the bin, it will absorb any humidity that gets inside and keep the filament dry.
You can also you silica beads or gel packs.
But if you really want to keep your filaments completely dry, the best thing you can do is buy a dehumidifier. Even a small one will make a big difference.





That’s pretty much all you need to do store most 3D printer filament for the long term. Put it in an airtight bin with a desiccant.
For more information about storing filament and extra tips to make sure your filament stays usable for a long time, check out our guide to 3D printer filament storage.
PART 7: 3D Printer Filament Accessories

Before you start printing, you can do a few accessories you can pick up that will make your printing experience easier. They save time and frustration, and over the course of several prints, their benefit can compound.
Other than the accessories listed below, most accessories are not strictly necessary for printing, but they are nice to have. Here is a quick list of a few other accessories to consider buying before you start printing.
Click here for a complete list of essential printer filament accessories.





PART 8: Best 3D printers

Most filaments will work on any FDM 3D printer. On rare occasions, some filaments will print better on specific 3D printers, but that is usually the result of human error or the quality of the 3D printer.
In general, good filament will print well on all good 3d printers if operated correctly.
Here’s a list of cheap 3D printers for under $300.



PART 9: Bad Filament? Troubleshooting failed prints
This topic is a bit outside of the normal scope of a 3D printer filament buyer’s guide but this information is important to have in case you do run into problems with the filament you buy.
The first step to troubleshooting failed prints is understanding what went wrong. So the goal here is to go through some of the most common reasons prints fail so that, if you are beginner, you cut down the amount of time it takes to find a solution.
There’s no universal way to troubleshoot all print failures becuase all printers are different and all printers are printing in different conditions with different materials. But understanding is the first step to finding a solution.
Clogs
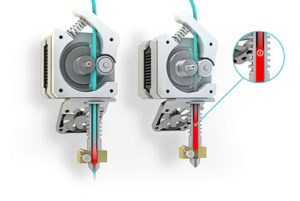
Clogs happen all the time in 3D printing. Clogging probably the most common issue 3D printers face.
And they are pain to deal with because so many things cause them: dirty gears, malfunctioning parts, obstructions in the hot end, printer height is too low, etc.
But when they are caused by filament, the problem is usually easier to discover. Here are a few of the most common reasons that 3D filament cause 3D printers to get clogged up.
- Particles in a specialty composite filament (wood, ceramic, metal) are too big to fit through the nozzle
- Impurities in the filament itself have either burned up inside the hotend or are obstructing the nozzle.
- Dirt or dust on the filament has entered the hot end and caused a jam
- Wood filament has burned up inside the hotend because the printer speed is too slow
- You didn’t clean out the extruder between spools so old filament is burning inside
- The momentum of the spool spinning forward has pushed more filament into the melt chamber than your printer can handle and has jammed it up.
- The filament absorbed too much water
- And last but not least (say it with me): THE DIAMETER OF THE FILAMENT IS TOO LARGE
Each of these issues has a different solutiont. But hopefully the list above has given you some ideas about what might be causing clogs you experience.
Solution: varies by printer, material, and environment
Warping

Warping is usually caused by uneven cooling between layers of filament. This happens commonly with ABS, PETG, and other filaments that require a heated printer bed and adhesive materials to keep the bottom of the object stuck to the print plate.
Basically, as middle layers cool, they contract, which pulls on the warm bottom layers that are in contact with the heated printer bed and the warm top layers that were recently extruded. If the force of the this contraction is large enough, the object will bend out of shape.
Solution: better bed adhesion and matching the print speed to the temperature of the print.
Delamination and Layer bonding

The same process described above can also pull layers apart. But layer bonding issues can have other causes as well.
Some 3D filaments simply don’t have good bonding properties. Flex filaments are a good example.
Other times, delamination occurs because the printer is speed is too slow and the filament isn’t getting deposited on top of the previous layer before it cools. After the previous layer cools, the new layer won’t won’t fuse with it as easily.
Discolorations

Some brands of filament have discolorations when printed. Discolored patches in object often occur when the colorant used in the filament is poor quality.
However, many discolorations are caused by impurities in the filament and by burned filament. PLA specifically becomes discolored when it absorbs too much moisture.
ABS and other plastics can also become discolored when exposed to UV rays and direct sunlight over time.
Fun Fact: The degradation of ABS by UV radiation in direct sunlight led to the discontinuation of it’s use in parts for seat belts in cars.
How to clean out your extruder with cleaning filament
If you haven’t tried eSUN cleaning filament already, then you are definitely missing out. That stuff is magical.
In fact, one of the best tips in this 3D Printer Filament Buyer’s Guide is to pick up a roll of cleaning filament immediately.
It will remove gunk from the inside of you printer that you didn’t even know was there. The best part about it is that it is super cheap and super easy to use.
Just push a 10 cm piece of it through your hotend while it is heated to the temperature you will be printing at. Then insert a piece of the material you want to print with and push the cleaning filament out. That’s it.
The cleaning filament will remove almost all dirt. It is far easier than other cleaning methods, like the Atomic pull method (AKA Cold pull or Nylon pull).
PART 10: Post-processing techniques for different materials

One of the advantages of making objects yourself with 3D printers is that you can customize them. That includes making sure they look exactly the way you want them to after they are printed.
After all, many objects come off the printer bed with visible layers, rough surfaces, discolorations and other imperfections. With a little touching up you can fix these blemishes and makes your pieces eye-catching.
Check here for a complete list of post-processing techniques for various materials.
Also, check out the list of post-processing solvents for ABS. There are more than you might imagine.
Table could not be displayed.PART 11: The Future Of Filament

We’re almost at the end of this 3D printer filament buyer’s guide. The last thing we need to talk about is the future.
The future of 3D printer filament looks very bright. As the 3D printing industry expands, the filament industry will as well.
Significant resources are being put towards developing new and innovative types of filament that will allow 3D printers to find new applications.
Several types of filament are already making waves in industries that are not traditionally focussed on plastics as a functional material. Architecture firms and other business that rely on rapid prototyping can now create prototypes in-house in just a few hours with PLA and ABS.
Conductive filaments hold strong promise for reshaping the future of the electronics industry. Ceramic filaments could change the way dishware, pottery, and ceramic parts are produced.

The filament industry is itself undergoing big changes. With the proliferation of cheap filament brands has come massive confusion about the quality of different filament products.
Soon, the 3D printing industry may shift in the direction of multimaterial printing (one printer, multiple extruders) and more specialized materials.
Moreover, with metal printing, bio printing, food printing and nano printing on the horizon, the filament industry will have to diversify to keep up. Innovative brands like Lay Filaments, owned by Kai Parthy, and Black Magic 3D, owned by Graphene 3D lab, will have to continue to innovate in order to stay relevant.
Meanwhile, larger filament brands will continue to hone their manufacturing technologies and large 3D printing companies will likely acquire promising filament brands. These trends could lead to market consolidation.

Perhaps the largest threat to filament companies is the rise of home extruders. Homemade filament is still in its infancy, and home filament extruders still face serious obstacles to widespread adoption.
But as the technology improves and prices come down, personal filament extruders could become the 3D filament source of choice for many, including the most hardcore DIY enthusiasts. Recycling trash into filament could become a daily chore for teenagers around world over the next decade.
Whatever happens, the consumer level 3D printing industry will more than double in the next 5 year according market analysts. That bodes well for the filament industry in general.
We will keep this 3D Printer Filament Buyer’s Guide updated with the latest information so that you can keep on top of these trends.
Final thoughts: 3D Printer Filament Buyer’s Guide
We hope you enjoyed this 3D printer filament buyer’s guide. We really did try to include everything a beginner would need to know about filament to get started.
Of course, 3D printer filament is such a wide subject that there are bound to be things we missed. If you would like us to include anything else, feel free to leave a comment below.
Happy printing!

Dear John
thanks a lot ..its Very important information
I want to know every new so please send me an email every new
I am an electrical and electronics engineer working in the field of media. I am interested in marketing these products in Saudi Arabia. I only want to study the idea in cooperation with you … I want to know the new versions of these devices and materials for 3D printers. We study the idea together. In Saudi Arabia I contribute in cooperation with you to find a agent
My name is Omar Alnskeeb
A friend of mine is thinking about buying a 3D printer, but we were curious about how to find the right filament first. I really like that you say to look at the quality, consistency, and price. I know that I would want to make sure that it’s going to be durable when purchasing, that way you make quality pieces.