Many different materials are used in the 3D printing, but the most common plastics are ABS and PLA. But what are the differences, and when should you choose PLA vs ABS?
As we mentioned in our review of best PLA filament brands, there is a lot of misinformation about PLA out there. For instance, some articles recommend brands that are actually scams, and others claim that PLA is food safe (technically yes, the plastic is food safe, but objects made of PLA are not food safe when printed with a consumer level FDM printer).
The situation is similar for ABS. You can learn more in our review of the best ABS filament brands currently available.
We are going to clear up all of the confusion here in this article once and for all, and explain exactly what the differences between PLA vs ABS are. So unless you looking for something else, like a full list of materials used in 3D printing, then you have come to the right place.
To get started, here is a quick comparison of the similarities and differences between ABS and PLA:


PLA
ABS

PLA

ABS
PLA vs ABS: Overview Of The Similarities and Differences
PLA and ABS are two of the most popular filaments for the basic reason that they are super easy to use. PLA is great for beginners, and ABS will be easy to learn after you have gained some experience with your 3D printer.
PLA and ABS are both thermoplastics, which means that they deform when heat is applied and then harden into their new shape when cooled. It is this property that makes them useful in FDM 3D printing since they can be extruded and shaped.
Check out the section below titled “What are thermoplastics?” for more information about these special plastics.
Together, PLA and ABS can be used for 90% of your projects. There are a few other types of plastics that you might wish to explore as well, such as PETG and Nylons, but for the most part, ABS and PLA are all you need.
PLA filaments – What You Need To Know
 PLA stands for Polylactic Acid. It is made from natural sources, such as corn starch in the USA or sugar cane in Asia. That means that PLA is also biodegradable, which is a unique and valuable characteristic to find in a plastic.
PLA stands for Polylactic Acid. It is made from natural sources, such as corn starch in the USA or sugar cane in Asia. That means that PLA is also biodegradable, which is a unique and valuable characteristic to find in a plastic.
Check out our review of the most eco-friendly filament brands to learn more about PLA and other types of biodegradable filaments.
PLA filament is compatible with all FDM 3D printers. PLA most often comes in the form of spools of filament wire, but you can also buy PLA in the form of pellets. Pellets are cheaper, but you will have to modify your printer to use them or make your own filament with a filament extruder.
The most important characteristic of a good filament is that it has the same thickness along the entire length of the filament. The accuracy of most filament brands, also called the tolerance, falls within the +/- 0.05mm range.
Some brands of PLA, such as Hatchbox, even have tolerances as low as +/- 0.02 mm.
Characteristics of PLA filaments
Because PLA is biodegradable, it isn’t suitable for making objects that will be outside or exposed to moisture. Over time rain, humidity or dampness will cause the PLA to melt or dissolve.
One of the best things about PLA is that it can be printed without the use of a heated printer bed, unlike ABS. That is because PLA doesn’t warp as easily as ABS and other thermoplastics do.
Because you will get less warping with PLA vs ABS, you don’t have to monitor your print as much or worry about having a high failure rate. Most of the time, PLA just works.
Although, active cooling with a fan does help to get good sharp edging. Set up a small fan and point it at your print bed, or attach a usb cooling fan to the printer directly.
ABS filaments – What You Need To Know
 ABS stands forAcrylonitrile butadiene styrene. It is made from oil-based sources, and is one of the most common plastics in consumer products. Everything from seatbelt buckles to TV remotes can be made of ABS.
ABS stands forAcrylonitrile butadiene styrene. It is made from oil-based sources, and is one of the most common plastics in consumer products. Everything from seatbelt buckles to TV remotes can be made of ABS.
Like PLA, ABS filament is compatible with all FDM 3D printers. ABS also comes in the form of spools of filament wire, and you can also buy ABS pellets.
ABS is a very popular filament for making objects that need to be durable and tough. Objects made with ABS will generally last much longer than objects made with PLA, especially in functional applications, such as when used to make electronics or mechanical parts.
Over the long term, ABS degrades in the sun, so keep in mind that it isn’t always suitable for making objects that will spend a lot of time outside. But unlike PLA, ABS is mostly water resistant and can be used to make objects that get wet often.
ABS Post-Processing Methods
Another bonus feature of ABS is that it is easy to make ABS prints look really good with post-processing using solvents. You can easily make rough surfaces of prints look smooth and shiny by giving them an acetone bath, as described in our article about solvents for ABS post-processing.
ABS warps easily so you need to use a heated print bed. The reason for this is that ABS, PLA and other thermoplastics cool unevenly after they are extruded.
Here’s what happens: the bottom of the printed object will cool faster than the higher layers and as the bottom layers cool, they contract, or shorten, while the warm upper layers are still expanding. This causes the print to bend out of shape and detach from the print bed.
A heated printer bed can help prevent warping with ABS, as can a good strong adhesive applied the print bed, such as glue stick or printer’s tape. Not all thermoplastics warp as much as others, however. For instance, you don’t need a heated printer bed to print with PLA.
ABS is simply a bit more finicky that PLA, and it’s difficulties like this that make ABS less suitable for beginners and more suitable for those who have a moderate amount of experience with 3D printing.
Quick Question: What Is A Thermoplastic?
 As mentioned above, PLA and ABS are both thermoplastics, which means that they are moldable and become soft easily when they are heated. Both PLA and ABS also solidify into their new shape when they are cooled.
As mentioned above, PLA and ABS are both thermoplastics, which means that they are moldable and become soft easily when they are heated. Both PLA and ABS also solidify into their new shape when they are cooled.
This heating and cooling process can be repeated several times and that makes PLA and ABS ideal materials for 3D printing.
So you may think that because PLA and ABS work so well, all thermoplastics can be used for 3D printing. But this isn’t true.
Characteristics of 3D printer materials
There are actually very few thermoplastics that can be used for 3D printing at the moment. In order for a material to be suitable for 3D printing, it needs to be fluid enough for extrusion, aesthetically pleasing, strong, and durable.
Specifically, these materials must have three characteristics when being tested for printing:
- The first extrusion into plastic filament must retain a the quality and color of the plastic
- The second extrusion as well as the trace binding during the process of 3D printing must again retain the quality and color of the original plastic source material
- The end use application and appropriateness as a 3D printed object or part must be useful to consumers. For example, no one will buy a filament if it can only be used to make a special type of engine gasket.
Moreover, there are many thermoplastics that have all of these 3 characteristics but are not as popular as ABS and PLA for 3D printing because they aren’t easy to print. For example, Nylon can be used in 3D printing, but it is harder to find the right temperature and settings to print it.
Of course, even though PLA and ABS have these great qualities in common, they are very different materials.
Next, let’s go deeper into the differences between PLA vs ABS.
PLA vs ABS: Comparative Analysis Of ABS and PLA Filaments
In the previous section, we laid out the basic differences and similarities between ABS and PLA that you need to know about before deciding which type of filament to buy.
Next, we are going to go over the specific details that make these two filaments unique. We are not going to get too technical with measurements of things like ductility and tensile strength.
However, this is where you will find specific advice for applications of ABS and PLA as well as what to expect when printing with them under specific condition. If you have questions about how to store PLA or ABS filaments or want more information about how to prevent warping, this in-depth analysis gives you the information you need.
To begin, let’s talk about strength and quality.

ABS vs PLA: Strength and Quality
PLA and ABS are both strong plastics. You can apply considerable force with your hands to objects printed with either PLA and ABS and get similar results in terms of strength and durability (provided that the infill is high and you aren’t pressing on an overhang or other fragile part).
Same thing goes for quality: both PLA and ABS both have pleasing surface finishes and color depth. You can also use various post-processing methods on both of them to improve the look and feels of finished prints.
ABS filament strength and quality
 ABS is known for being very strong and hard. The most famous example use of ABS is in Lego pieces.
ABS is known for being very strong and hard. The most famous example use of ABS is in Lego pieces.
As anyone who has ever stepped on a Lego piece in bare feet knows, Legos are hard and their corners will remain pointy even when large amount of force are applied to them.
This makes ABS ideal for functional applications and objects that need to withstand significant stress, like light switches, children’s toys, and some kinds of jewelry.
ABS Is Strong And Looks Great
Even with fairly low infill percentages, ABS objects remain hard and strong relative to PLA. When it comes to strength in the PLA vs ABS filament debate, ABS wins every time.
ABS is also well known for having a very pleasing surface finish when post-processed with Acetone. Acetone, which is the main ingredient in nail polish remover, melts ABS and can be used to smooth the layer lines on the surface of ABS prints.
Not all ABS needs to be given an Acetone bath, however. Some ABS filaments contain additives that produce a shiny surface directly after printing, such as Hatchbox Black ABS. But most ABS filaments will respond well to treatment with Acetone.
PLA filament strength and quality
 PLA is known for being medium to high strength, but certainly not as strong as ABS. Still, you can print most plastic objects with it and expect these objects to withstand most reasonable applications of force.
PLA is known for being medium to high strength, but certainly not as strong as ABS. Still, you can print most plastic objects with it and expect these objects to withstand most reasonable applications of force.
The strength of PLA can also be vastly improved with high infill percentages. If you set the infill to 70% or more on your PLA prints, you can be sure to get very strong parts and objects.
PLA is also very pleasing to the eye. The surface finish isn’t usually as shiny as ABS, but that doesn’t detract from the overall pleasing coloration and smooth look of PLA prints.
Combined with the ease of use and general durability, the look and feel of PLA makes it the preferred thermoplastic filament for both beginners and expert 3D printers alike.
ABS vs PLA Storage

When it comes to storing PLA vs ABS, there aren’t too many differences. ABS and PLA can both be stored the same way: in air tight plastic containers.
You can also hang filaments on a bar above your work bench or stack them on shelves. But if you leave them exposed directly to the air, then you need to control the humidity in the room you work in.
Even if you store the filament inside of a plastic bag, unless you vacuum seal it, that is only one layer of plastic between the air and your filament.
Therefore, you need to buy a humidifier. A humidifier is a fantastic way to control humidity in your work space.
Check out our run-down of the best humidifiers for the room you store your 3D printing materials in.
You need to be especially careful when storing PLA vs ABS. Why do you need to control the moisture around your filament?
Read on for a full explanation.
PLA vs ABS: ABS Storage – How To Store ABS

The best way to store ABS is inside of a plastic storage bin that is airtight. The best kind of bins are large enough to hold around 5 to 10 spools.
Also, clear bins allow you to see the colors, types and brands of the ABS filaments inside. Also make sure to get bins that snap shut, not bins with lids that simply sit on top with nothing attaching it.
The reason is that plastic bins will warp over time, and unless there is some mechanism for holding the lid to the rim of the bins, the bin and lid will warp and gaps will open and let air in.
You can also put ABS inside vacuum sealed bags. There are fantastic vacuum sealing bags for sale on Amazon.
Otherwise, your best bet is too keep ABS filaments somewhere dry and free of dust. The best open air conditions for storing ABS would include a temperature controlled, dust free environment, such as shelf in a room that has a central air conditioning unit. Air conditioners and dehumidifiers work really well also.
What Happens When ABS Gets Wet?

ABS tends to bubble and splutter from the tip of a nozzle while printing when wet. You can hear it crackling and popping as it extrudes.
This spluttering reduces the visual quality of the part as well as the strength and accuracy of the part. It can also clog your nozzle and create a mess inside your extruder.
Also, be careful not to let your ABS sit in the sun for long periods of time. Over time, the ABS will change colors and become more brittle, as you can see in the photo above.
 QUICK FIX: But thankfully, ABS is usually easily dried by applying heat in a controlled manner. A light warm breeze from a hair dryer works like a charm.
QUICK FIX: But thankfully, ABS is usually easily dried by applying heat in a controlled manner. A light warm breeze from a hair dryer works like a charm.
You can also try heating appliances such as ovens and food dehydrators. Just make sure to keep the heat settings low to avoid melting the ABS plastic and causing the tolerances and ovality (shape) of the filament to warp.
PLA vs ABS: PLA Storage – How To Store PLA

The best way to store PLA is also inside of clear, air-tight plastic bins. The plastic bins on Amazon are fantastic and cheap, but most importantly, they also stack.
Stackable bins allow you to store the bins in closets and save floor space.
Because PLA is so susceptible to absorbing moisture it is extremely important to keep a desiccant of some kind near your PLA filaments, even inside of vacuum sealed plastic bags or air-tight storage containers. Desiccants are chemicals that absorb water from the air and protect other objects from humidity or moisture.
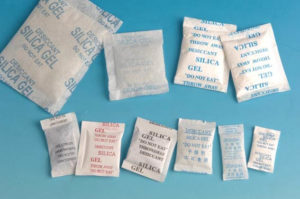
Some of the most popular desiccants include silicon desiccant packets and rice. Desiccant packets fit fight into the spool hole of a roll of filament and can be easily included in any storage container as a result, including vacuum sealed bags.
If you don’t have access to desiccant packets, you can put your PLA plastic filament into a bin, then include some rice in an open jar or bowl inside of the bin. The rice will absorb all of the humidity inside the bin and protect your PLA filament.
PLA vs ABS: What Happens When PLA Gets Wet?
PLA will also absorb moisture like a sponge. Similarly to ABS, PLA will bubble and splutter from the nozzle when it is wet.
In fact, PLA immediately begins to degrade when it comes in contact with water molecules, and PLA filament that has been in contact with water for too long will completely dissolve.
QUICK FIX: However, if caught early, PLA can be dried and quality restored. This has to do with the fact that water doesn’t bind with PLA polymer molecules immediately. The process is gradual.
So if your PLA hasn’t been wet for too long, dry it out with a hair dryer and it might be good as new.
If a hair drier doesn’t do the trick, try putting PLA in an oven or food dehydrator on a low heat for a little while.
PLA vs ABS: PLA and ABS Smell
Overall, most people tend to prefer the smell of PLA vs ABS. It’s just
ABS Smell
ABS Filament smells like hot plastic when it is being printed, and some find it rather unbearable. For this reason alone, many people prefer PLA vs ABS.
It is important to remember that good ventilation is key for operating 3D printers, especially in small rooms when printing with an ABS filament. Otherwise, ABS fumes could be dangerous and cause irritations to your eyes and lungs.
PLA Smell
PLA filament has a semi-sweet smell due to it being formed from sugar. It smells similar to a sweet cooking oil and is preferred over ABS’s hot plastic smell for most.
PLA filament is also less likely to irritate your eyes, nose and throat than ABS. Furthermore, the smell of PLA is mild enough that is doesn’t over power other exotic filaments such as wood PLA or specialty frangrant / perfumed PLA.
PLA vs ABS: Warping of ABS and PLA Filaments
Both PLA and ABS are more than capable of making dimensionally accurate parts. Here are a few differences between PLA vs ABS that you may want to take a look at:
ABS Warping
 ABS has a tendency to have an issue with curling upwards on the surface in direct touch with the printer’s print bed. This problem is called warping and can be resolved with a combination of two precautions:
ABS has a tendency to have an issue with curling upwards on the surface in direct touch with the printer’s print bed. This problem is called warping and can be resolved with a combination of two precautions:
- Heat the printing surface to ensure that the first few layers of the printed object don’t cool faster than the rest of the object.
- Apply an adhesive to the printer bed in order to hold the bottom layers in place to prevent curling upward.
A fan can also be used to actively cool the plastic and ensure that the ABS material does not round on the corners if you are attempting to get a sharp edge. Beware, the active cooling can increase the risk of reducing adhesion between layers which end up in cracks.
PLA Warping
PLA has much less warping of parts and allows you to successfully print without a heated bed. However, you might not want to remove the heated bed for larger pieces that take longer to print since the bottom of the print could curl up over time. Use your best judgment.
Also active cooling with a fan pointed at the printer bed can cool the printed object faster and increase the resolution of details. Often, pointing a fan at the print can help keep corners sharp.
PLA vs ABS: Best PLA Filaments
At this point, you might be wondering, “where do I find PLA filaments that are good quality?”
The following list is a good place to start. Most beginners should start with PLA, since printing is easier with PLA vs ABS.
These are some of the best PLA filament brands available. It is just a quick overview of the highlights for each brand, but there is a lot more to say.
To learn more about them and see a few other options, check our review of the best PLA filament brands.
eSUN PLA Filament
eSUN filament is a fantastic, cheap PLA filament that is widely regarded as an industry standard filament for both small businesses and consumers. It comes from China and is sometimes rebranded as Inland filament.
This is a great filament to start with for beginners. Read our full review of eSUN here and our full review of Inland here.
IC3D PLA Filament
IC3D PLA filament is made in the United States and has become one of the most popular products on the market.
It has a diameter within +/- 0.05mm with a roundness of 4%. Each spool is hand-checked and the success of this PLA filament can be seen in the high quality results. It also comes with a 100% satisfaction guarantee.
HATCHBOX PLA Filament
This product is designed to help you reap the rewards of an accurate and aesthetically pleasing 3D object print. It holds a diameter of 1.75mm and has a dimensional accuracy of +/- 0.02mm.
Hatchbox is absolutely the number 1 most popular brand of filament and well worth trying if you haven’t already. Check out the thousands of reviews that Hatchbox filaments get on Amazon
PLA vs ABS: Best ABS Filament
HATCHBOX ABS Filament
Hatchbox ABS is one of the post popular ABS filaments on Amazon. Made in China and sold in the US, Hatchbox is one of the few filament brands from China that has achieved the highest quality and consistency standards that 3D printers expect.
Hatchbox also has fantastic spool design, packaging and return policies. Check out of full review to learn more about Hatchbox.
eSUN ABS
eSUN ABS filament is compatible with 3D printers that use a 1.75mm diameter filament. It is tough, durable and is designed to be used on 3D prints that need to be strong and visually appealing.
The recommended nozzle temperature is between 220 and 260 degrees Fahrenheit, which is more forgiving range than other similar ABS filaments.
IC3D ABS
IC3D ABS filament is another go-to ABS filament from a brand that has established itself as a leader in the filament industry. Like other filaments of this caliber, it has an extremely consistent tolerance of +/- 0.05mm.
Each spool is hand-checked and comes with a 100% satisfaction guarantee.
PLA vs ABS: Final Thoughts
ABS and PLA are very different thermoplastics and require different settings to print with. They are both susceptible to degrading when wet so make sure to control the humidity around them when you store them.
Moisture regulation in storage is often the most difficult aspect of working with these materials.
There are also a wide range of brands to choose from. Many brands produce top quality ABS and PLA, and it is not always clear what the best PLA and ABS filaments are.
However, if you stick with the brands on this list, you won’t be disappointed.
Hopefully this was a useful discussion of the differences between PLA vs ABS. If you have any questions of comments, or if we missed anything in this article, leave a comment below.
Otherwise, thank you for reading, and happy printing!







